Subpart U—Special Flight Rules in the Vicinity of Grand Canyon National Park, AZ
- § 93.301 Applicability.
- § 93.303 Definitions.
- § 93.305 Flight-free zones and flight corridors.
- § 93.307 Minimum flight altitudes.
- § 93.309 General operating procedures.
- § 93.311 Minimum terrain clearance.
- § 93.313 Communications.
- § 93.315 Requirements for commercial Special Flight Rules Area operations.
- § 93.316 [Reserved]
- § 93.317 Commercial Special Flight Rules Area operation curfew.
- § 93.319 Commercial air tour limitations.
- § 93.321 Transfer and termination of allocations.
- § 93.323 [Reserved
- § 93.325 Quarterly reporting.
- Appendix to Subpart U of Part 93—Special Flight Rules in the Vicinity of the Grand Canyon National Park, AZ
- Appendix A to Subpart U of Part 93—GCNP Quiet Aircraft Technology Designation
§ 93.301 Applicability.
This subpart prescribes special operating rules for all persons operating aircraft in the following airspace, designated as the Grand Canyon National Park Special Flight Rules Area: That airspace extending from the surface up to but not including 18,000 feet MSL within an area bounded by a line beginning at Lat. 35°55′12″ N., Long. 112°04′05″ W.; east to Lat. 35°55′30″ N., Long. 111°45′00″ W.; to Lat. 35°59′02″ N., Long. 111°36′03″ W.; north to Lat. 36°15′30″ N., Long. 111°36′06″ W.; to Lat. 36°24′49″ N., Long. 111°47′45″ W.; to Lat. 36°52′23″ N., Long. 111°33′10″ W.; west-northwest to Lat. 36°53′37″ N., Long. 111°38′29″ W.; southwest to Lat. 36°35′02″ N., Long. 111°53′28″ W.; to Lat. 36°21′30″ N., Long. 112°00′03″ W.; west-northwest to Lat. 36°30′30″ N., Long. 112°35′59″ W.; southwest to Lat. 36°24′46″ N., Long. 112°51′10″ W., thence west along the boundary of Grand Canyon National Park (GCNP) to Lat. 36°14′08″ N., Long. 113°10′07″ W.; west-southwest to Lat. 36°09′30″ N., Long. 114°03′03″ W.; southeast to Lat. 36°05′11″ N., Long. 113°58′46″ W.; thence south along the boundary of GCNP to Lat. 35°58′23″ N., Long. 113°54′14″ W.; north to Lat. 36°00′10″ N., Long. 113°53′48″ W.; northeast to Lat. 36°02′14″ N., Long. 113°50′16″ W.; to Lat. 36°02′17″ N., Long. 113°53′48″ W.; northeast to Lat. 36°02′14″ N., Long. 113°50′16″ W.; to Lat. 36°02′17″ N., Long. 113°49′11″ W.; southeast to Lat. 36°01′22″ N., Long. 113°48′21″ W.; to Lat. 35°59′15″ N., Long. 113°47′13″ W.; to Lat. 35°57′51″ N., Long. 113°46′01″ W.; to Lat. 35°57′45″ N., Long. 113°45′23″ W.; southwest to Lat. 35°54′48″ N., Long. 113°50′24″ W.; southeast to Lat. 35°41′01″ N., Long. 113°35′27″ W.; thence clockwise via the 4.2-nautical mile radius of the Peach Springs VORTAC to Lat. 36°38′53″ N., Long. 113°27′49″ W.; northeast to Lat. 35°42′58″ N., Long. 113°10′57″ W.; north to Lat. 35°57′51″ N., Long. 113°11′06″ W.; east to Lat. 35°57′44″ N., Long. 112°14′04″ W.; thence clockwise via the 4.3-nautical mile radius of the Grand Canyon National Park Airport reference point (Lat. 35°57′08″ N., Long. 112°08′49″ W.) to the point of origin.
§ 93.303 Definitions.
For the purposes of this subpart:
Allocation means authorization to conduct a commercial air tour in the Grand Canyon National Park (GCNP) Special Flight Rules Area (SFRA).
Commercial air tour means any flight conducted for compensation or hire in a powered aircraft where a purpose of the flight is sightseeing. If the operator of a flight asserts that the flight is not a commercial air tour, factors that can be considered by the Administrator in making a determination of whether the flight is a commercial air tour include, but are not limited to—
(1) Whether there was a holding out to the public of willingness to conduct a sightseeing flight for compensation or hire;
(2) Whether a narrative was provided that referred to areas or points of interest on the surface;
(3) The area of operation;
(4) The frequency of flights;
(5) The route of flight;
(6) The inclusion of sightseeing flights as part of any travel arrangement package; or
(7) Whether the flight in question would or would not have been canceled based on poor visibility of the surface.
Commercial Special Flight Rules Area Operation means any portion of any flight within the Grand Canyon National Park Special Flight Rules Area that is conducted by a certificate holder that has operations specifications authorizing flights within the Grand Canyon National Park Special Flight Rules Area. This term does not include operations conducted under an FAA Form 7711–1, Certificate of Waiver or Authorization. For more information on commercial special flight rules area operations, see “Grand Canyon National Park Special Flight Rules Area (GCNP SFRA) Procedures Manual,” which is available online or from the responsible Flight Standards Office.
GCNP quiet aircraft technology designation means an aircraft that is subject to § 93.301 and has been shown to comply with the noise limit specified in appendix A of this part.
Number of passenger seats means the number of passenger seats for which an individual aircraft is configured.
Park means Grand Canyon National Park.
Special Flight Rules Area means the Grand Canyon National Park Special Flight Rules Area.
§ 93.305 Flight-free zones and flight corridors.
Except in an emergency or if otherwise necessary for safety of flight, or unless otherwise authorized by the responsible Flight Standards Office for a purpose listed in § 93.309, no person may operate an aircraft in the Special Flight Rules Area within the following flight-free zones:
(a) Desert View Flight-free Zone. That airspace extending from the surface up to but not including 14,500 feet MSL within an area bounded by a line beginning at Lat. 35°59′58″ N., Long. 111°52′47″ W.; thence east to Lat. 36°00′00″ N., Long. 111°51′04″ W.; thence north to 36°00′24″ N., Long. 111°51′04″ W.; thence east to 36°00′24″ N., Long. 111°45′44″ W.; thence north along the GCNP boundary to Lat. 36°14′05″ N., Long. 111°48′34″ W.; thence southwest to Lat. 36°12′06″ N., Long. 111°51′14″ W.; to the point of origin; but not including the airspace at and above 10,500 feet MSL within 1 nautical mile of the western boundary of the zone. The corridor to the west between the Desert View and Bright Angel Flight-free Zones, is designated the “Zuni Point Corridor.” This corridor is 2 nautical miles wide for commercial air tour flights and 4 nautical miles wide for transient and general aviation operations.
(b) Bright Angel Flight-free Zone. That airspace extending from the surface up to but not including 14,500 feet MSL within an area bounded by a line beginning at Lat. 35°58′39″ N., Long. 111°55′43″ W.; north to Lat. 36°12′41″ N., Long. 111°53′54″ W.; northwest to Lat. 36°18′18″ N., Long. 111°58′15″ W.; thence west along the GCNP boundary to Lat. 36°20′11″ N., Long. 112°06′25″ W.; south-southwest to Lat. 36°09′31″ N., Long. 112°11′15″ W.; to Lat. 36°04′16″ N., Long. 112°17′20″ W.; thence southeast along the GCNP boundary to Lat. 36°01′54″ N., Long. 112°11′24″ W.; thence clockwise via the 4.3-nautical mile radius of the Grand Canyon National Park Airport reference point (Lat. 35°57′08″ N., Long. 112°08′49″ W.) to Lat. 35°59′37″ N., Long. 112°04′29″ W.; thence east along the GCNP boundary to the point of origin; but not including the airspace at and above 10,500 feet MSL within 1 nautical mile of the eastern boundary or the airspace at and above 10,500 feet MSL within 2 nautical miles of the northwestern boundary. The corridor to the east, between this flight-free zone and the Desert View Flight-free Zone, is designated the “Zuni Point Corridor.” The corridor to the west, between the Bright Angel and Toroweap/Shinumo Flight-free Zones, is designated the “Dragon Corridor.” This corridor is 2 nautical miles wide for commercial air tour flights and 4 nautical miles wide for transient and general aviation operations. The Bright Angel Flight-free Zone does not include the following airspace designated as the Bright Angel Corridor: That airspace one-half nautical mile on either side of a line extending from Lat. 36°14′57″ N., Long. 112°08′45″ W. and Lat. 36°15′01″ N., Long. 111°55′39″ W.
(c) Toroweap/Shinumo Flight-free Zone. That airspace extending from the surface up to but not including 14,500 feet MSL within an area bounded by a line beginning at Lat. 36°05′44″ N., Long. 112°19′27″ W.; north-northeast to Lat. 36°10′49″ N., Long. 112°13′19″ W.; to Lat. 36°21′02″ N., Long. 112°08′47″ W.; thence west and south along the GCNP boundary to Lat 36°10′58″ N., Long. 113°08′35″ W.; south to Lat. 36°10′12″ N., Long. 113°08′34″ W.; thence in an easterly direction along the park boundary to the point of origin; but not including the following airspace designated as the “Tuckup Corridor”: at or above 10,500 feet MSL within 2 nautical miles either side of a line extending between Lat. 36°24′42″ N., Long. 112°48′47″ W. and Lat. 36°14′17″ N., Long. 112°48′31″ W. The airspace designated as the “Fossil Canyon Corridor” is also excluded from the Toroweap/Shinumo Flight-free Zone at or above 10,500 feet MSL within 2 nautical miles either side of a line extending between Lat. 36°16′26″ N., Long. 112°34′35″ W. and Lat. 36°22′51″ N., Long. 112°18′18″ W. The Fossil Canyon Corridor is to be used for transient and general aviation operations only.
(d) Sanup Flight-free Zone. That airspace extending from the surface up to but not including 8,000 feet MSL within an area bounded by a line beginning at Lat. 35°59′32″ N., Long. 113°20′28″ W.; west to Lat. 36°00′55″ N., Long. 113°42′09″ W.; southeast to Lat. 35°59′57″ N., Long. 113°41′09″ W.; to Lat. 35°59′09″ N., Long. 113°40′53″ W.; to Lat. 35°58′45″ N., Long. 113°40′15″ W.; to Lat. 35°57′52″ N., Long. 113°39′34″ W.; to Lat. 35°56′44″ N., Long. 113°39′07″ W.; to Lat. 35°56′04″ N., Long. 113°39′20″ W.; to Lat. 35°55′02″ N., Long. 113°40′43″ W.; to Lat. 35°54′47″ N., Long. 113°40′51″ W.; southeast to Lat. 35°50′16″ N., Long. 113°37′13″ W.; thence along the park boundary to the point of origin.
§ 93.307 Minimum flight altitudes.
Except in an emergency, or if otherwise necessary for safety of flight, or unless otherwise authorized by the responsible Flight Standards Office for a purpose listed in § 93.309, no person may operate an aircraft in the Special Flight Rules Area at an altitude lower than the following:
(a) Minimum sector altitudes —
(1) Commercial air tours —
(i) Marble Canyon Sector. Lees Ferry to Boundary Ridge: 6,000 feet MSL.
(ii) Supai Sector. Boundary Ridge to Supai Point: 7,500 feet MSL.
(iii) Diamond Creek Sector. Supai Point to Diamond Creek: 6,500 feet MSL.
(iv) Pearce Ferry Sector. Diamond Creek to the Grand Wash Cliffs: 5,000 feet MSL.
(2) Transient and general aviation operations —
(i) Marble Canyon Sector. Lees Ferry to Boundary Ridge: 8,000 feet MSL.
(ii) Supai Sector. Boundary Ridge to Supai Point: 10,000 feet MSL.
(iii) Diamond Creek Sector. Supai Point to Diamond Creek: 9,000 feet MSL.
(iv) Pearce Ferry Sector. Diamond Creek to the Grand Wash Cliffs: 8,000 feet MSL.
(b) Minimum corridor altitudes —
(1) Commercial air tours —
(i) Zuni Point Corridors. 7,500 feet MSL.
(ii) Dragon Corridor. 7,500 feet MSL.
(2) Transient and general aviation operations —
(i) Zuni Point Corridor. 10,500 feet MSL.
(ii) Dragon Corridor. 10,500 feet MSL.
(iii) Tuckup Corridor. 10,500 feet MSL.
(iv) Fossil Canyon Corridor. 10,500 feet
§ 93.309 General operating procedures.
Except in an emergency, no person may operate an aircraft in the Special Flight Rules Area unless the operation is conducted in accordance with the following procedures. ( Note: The following procedures do not relieve the pilot from see-and-avoid responsibility or compliance with the minimum safe altitude requirements specified in § 91.119 of this chapter.):
(a) Unless necessary to maintain a safe distance from other aircraft or terrain remain clear of the flight-free zones described in § 93.305;
(b) Unless necessary to maintain a safe distance from other aircraft or terrain, proceed through the Zuni Point, Dragon, Tuckup, and Fossil Canyon Flight Corridors described in § 93.305 at the following altitudes unless otherwise authorized in writing by the responsible Flight Standards Office:
(1) Northbound. 11,500 or 13,500 feet MSL.
(2) Southbound. 10,500 or 12,500 feet MSL.
(c) For operation in the flight-free zones described in § 93.305, or flight below the altitudes listed in § 93.307, is authorized in writing by the responsible Flight Standards Office and is conducted in compliance with the conditions contained in that authorization. Normally authorization will be granted for operation in the areas described in § 93.305 or below the altitudes listed in § 93.307 only for operations of aircraft necessary for law enforcement, firefighting, emergency medical treatment/evacuation of persons in the vicinity of the Park; for support of Park maintenance or activities; or for aerial access to and maintenance of other property located within the Special Flight Rules Area. Authorization may be issued on a continuing basis;
(d) Is conducted in accordance with a specific authorization to operate in that airspace incorporated in the operator's operations specifications and approved by the responsible Flight Standards Office in accordance with the provisions of this subpart;
(e) Is a search and rescue mission directed by the U.S. Air Force Rescue Coordination Center;
(f) Is conducted within 3 nautical miles of Grand Canyon Bar Ten Airstrip, Pearce Ferry Airstrip, Cliff Dwellers Airstrip, Marble Canyon Airstrip, or Tuweep Airstrip at an altitude less than 3,000 feet above airport elevation, for the purpose of landing at or taking off from that facility; or
(g) Is conducted under an instrument flight rules (IFR) clearance and the pilot is acting in accordance with ATC instructions. An IFR flight plan may not be filed on a route or at an altitude that would require operation in an area described in § 93.305.
§ 93.311 Minimum terrain clearance.
Except in an emergency, when necessary for takeoff or landing, or unless otherwise authorized by the responsible Flight Standards Office for a purpose listed in § 93.309(c), no person may operate an aircraft within 500 feet of any terrain or structure located between the north and south rims of the Grand Canyon.
§ 93.313 Communications.
Except when in contact with the Grand Canyon National Park Airport Traffic Control Tower during arrival or departure or on a search and rescue mission directed by the U.S. Air Force Rescue Coordination Center, no person may operate an aircraft in the Special Flight Rules Area unless he monitors the appropriate frequency continuously while in that airspace.
§ 93.315 Requirements for commercial Special Flight Rules Area operations.
Each person conducting commercial Special Flight Rules Area operations must be certificated in accordance with Part 119 for Part 135 or 121 operations and hold appropriate Grand Canyon National Park Special Flight Rules Area operations specifications.
§ 93.316 [Reserved]
"[Reserved]" is used simply to indicate that regulatory information might be inserted into this location at some time in the future, and is a placeholder to indicate that the section was intentionally left blank, and not dropped due to a computer error.
§ 93.317 Commercial Special Flight Rules Area operation curfew.
Unless otherwise authorized by the responsible Flight Standards Office, no person may conduct a commercial Special Flight Rules Area operation in the Dragon and Zuni Point corridors during the following flight-free periods:
(a) Summer season (May 1–September 30)–6 p.m. to 8 a.m. daily; and
(b) Winter season (October 1–April 30)–5 p.m. to 9 a.m. daily.
§ 93.319 Commercial air tour limitations.
(a) Unless excepted under paragraph (f) or (g) of this section, no certificate holder certificated in accordance with part 119 for part 121 or 135 operations may conduct more commercial air tours in the Grand Canyon National Park in any calendar year than the number of allocations specified on the certificate holder's operations specifications.
(b) The Administrator determines the number of initial allocations for each certificate holder based on the total number of commercial air tours conducted by the certificate holder and reported to the FAA during the period beginning on May 1, 1997 and ending on April 30, 1998, unless excepted under paragraph (g).
(c) Certificate holders who conducted commercial air tours during the base year and reported them to the FAA receive an initial allocation.
(d) A certificate holder must use one allocation for each flight that is a commercial air tour, unless excepted under paragraph (f) or (g) of this section.
(e) Each certificate holder's operation specifications will identify the following information, as applicable:
(1) Total SFRA allocations; and
(2) Dragon corridor and Zuni Point corridor allocations.
(f) Certificate holders satisfying the requirements of § 93.315 of this subpart are not required to use a commercial air tour allocation for each commercial air tour flight in the GCNP SFRA provided the following conditions are satisfied:
(1) The certificate holder conducts its operations in conformance with the routes and airspace authorizations as specified in its Grand Canyon National Park Special Flight Rules Area operations specifications;
(2) The certificate holder must have executed a written contract with the Hualapai Indian Nation which grants the certificate holder a trespass permit and specifies the maximum number of flights to be permitted to land at Grand Canyon West Airport and at other sites located in the vicinity of that airport and operates in compliance with that contract; and
(3) The certificate holder must have a valid operations specification that authorizes the certificate holder to conduct the operations specified in the contract with the Hualapai Indian Nation and specifically approves the number of operations that may transit the Grand Canyon National Park Special Flight Rules Area under this exception.
(g) Certificate holders conducting commercial air tours at or above 14,500 feet MSL but below 18,000 feet MSL who did not receive initial allocations in 1999 because they were not required to report during the base year may operate without an allocation when conducting air tours at those altitudes. Certificate holders conducting commercial air tours in the area affected by the eastward shift of the SFRA who did not receive initial allocations in 1999 because they were not required to report during the base year may continue to operate on the specified routes without an allocation in the area bounded by longitude line 111 degrees 42 minutes east and longitude line 111 degrees 36 minutes east. This exception does not include operation in the Zuni Point corridor.
§ 93.321 Transfer and termination of allocations.
(a) Allocations are not a property interest; they are an operating privilege subject to absolute FAA control.
(b) Allocations are subject to the following conditions:
(1) The Administrator will re-authorize and re-distribute allocations no earlier than two years from the effective date of this rule.
(2) Allocations that are held by the FAA at the time of reallocation may be distributed among remaining certificate holders, proportionate to the size of each certificate holder's allocation.
(3) The aggregate SFRA allocations will not exceed the number of operations reported to the FAA for the base year beginning on May 1, 1997 and ending on April 30, 1998, except as adjusted to incorporate operations occurring for the base year of April 1, 2000 and ending on March 31, 2001, that operate at or above 14,500 feet MSL and below 18,000 feet MSL and operations in the area affected by the eastward shift of the SFRA bounded by longitude line 111 degrees 42 minutes east to longitude 111 degrees 36 minutes east.
(4) Allocations may be transferred among Part 135 or Part 121 certificate holders, subject to all of the following:
(i) Such transactions are subject to all other applicable requirements of this chapter.
(ii) Allocations authorizing commercial air tours outside the Dragon and Zuni Point corridors may not be transferred into the Dragon and Zuni Point corridors. Allocations authorizing commercial air tours within the Dragon and Zuni Point corridors may be transferred outside of the Dragon and Zuni Point corridors.
(iii) A certificate holder must notify in writing the responsible Flight Standards Office within 10 calendar days of a transfer of allocations. This notification must identify the parties involved, the type of transfer (permanent or temporary) and the number of allocations transferred. Permanent transfers are not effective until the responsible Flight Standards Office reissues the operations specifications reflecting the transfer. Temporary transfers are effective upon notification.
(5) An allocation will revert to the FAA upon voluntary cessation of commercial air tours within the SFRA for any consecutive 180-day period unless the certificate holder notifies the FSDO in writing, prior to the expiration of the 180-day time period, of the following: the reason why the certificate holder has not conducted any commercial air tours during the consecutive 180-day period; and the date the certificate holder intends on resuming commercial air tours operations. The FSDO will notify the certificate holder of any extension to the consecutive 180-days. A certificate holder may be granted one extension.
(6) The FAA retains the right to re-distribute, reduce, or revoke allocations based on:
(i) Efficiency of airspace;
(ii) Voluntary surrender of allocations;
(iii) Involuntary cessation of operations; and
(iv) Aviation safety.
§ 93.323 [Reserved
§ 93.325 Quarterly reporting.
(a) Each certificate holder must submit in writing, within 30 days of the end of each calendar quarter, the total number of commercial SFRA operations conducted for that quarter. Quarterly reports must be filed with the responsible Flight Standards Office.
(b) Each quarterly report must contain the following information.
(1) Make and model of aircraft;
(2) Identification number (registration number) for each aircraft;
(3) Departure airport for each segment flown;
(4) Departure date and actual Universal Coordinated Time, as applicable for each segment flown;
(5) Type of operation; and
(6) Route(s) flown.
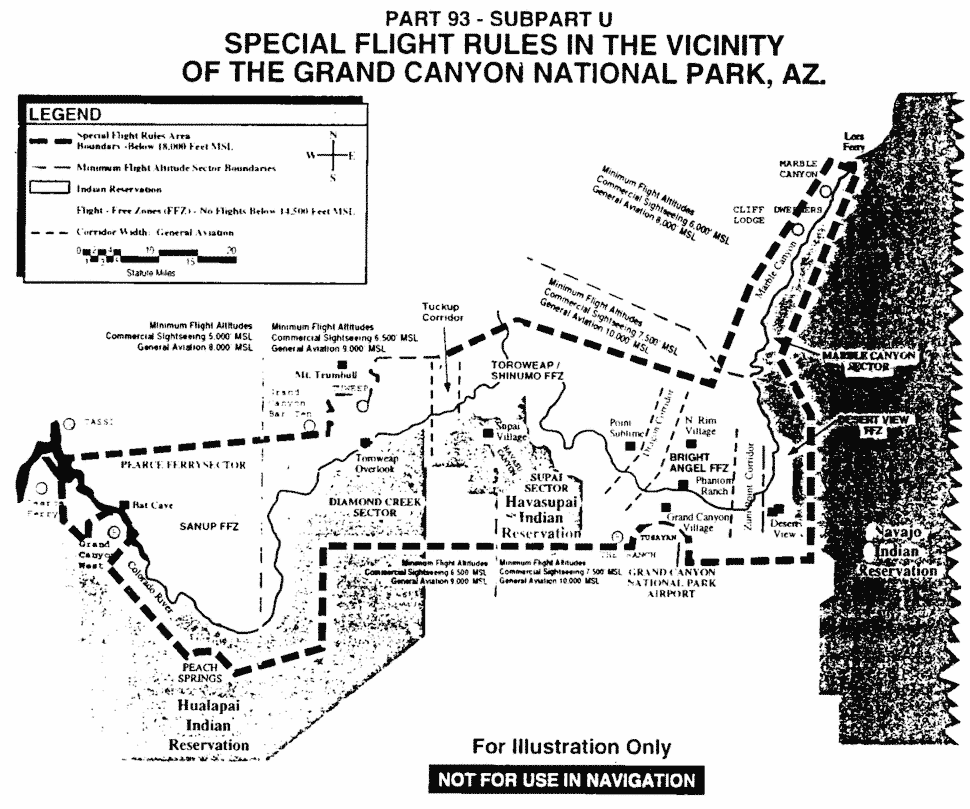
Appendix to Subpart U of Part 93—Special Flight Rules in the Vicinity of the Grand Canyon National Park, AZ
Appendix A to Subpart U of Part 93—GCNP Quiet Aircraft Technology Designation
This appendix contains procedures for determining the GCNP quiet aircraft technology designation status for each aircraft subject to § 93.301 determined during the noise certification process as prescribed under part 36 of this chapter. Where no certificated noise level is available, the Administrator may approve an alternative measurement procedure.
Aircraft Noise Limit for GCNP Quiet Aircraft Technology Designation
A. For helicopters with a flyover noise level obtained in accordance with the measurement procedures prescribed in Appendix H of 14 CFR part 36, the limit is 80 dB for helicopters having a seating configuration of two or fewer passenger seats, increasing at 3 dB per doubling of the number of passenger seats for helicopters having a seating configuration of three or more passenger seats. The noise limit for helicopters with three or more passenger seats can be calculated by the formula:
EPNL(H) = 80 + 10log(# PAX seats/2) dB
B. For helicopters with a flyover noise level obtained in accordance with the measurement procedures prescribed in Appendix J of 14 CFR part 36, the limit is 77 dB for helicopters having a seating configuration of two or fewer passenger seats, increasing at 3 dB per doubling of the number of passenger seats for helicopters having a seating configuration of three or more passenger seats. The noise limit for helicopters with three or more passenger seats can be calculated by the formula:
SEL(J) = 77 + 10log(# PAX seats/2) dB
C. For propeller-driven airplanes with a measured flyover noise level obtained in accordance with the measurement procedures prescribed in Appendix F of 14 CFR part 36 without the performance correction defined in Sec. F35.201(c), the limit is 69 dB for airplanes having a seating configuration of two or fewer passenger seats, increasing at 3 dB per doubling of the number of passenger seats for airplanes having a seating configuration of three or more passenger seats. The noise limit for propeller-driven airplanes with three or more passenger seats can be calculated by the formula:
LAmax(F) = 69 + 10log(# PAX seats/2) dB
D. In the event that a flyover noise level is not available in accordance with Appendix F of 14 CFR part 36, the noise limit for propeller-driven airplanes with a takeoff noise level obtained in accordance with the measurement procedures prescribed in Appendix G is 74 dB or 77 dB, depending on 14 CFR part 36 amendment level, for airplanes having a seating configuration of two or fewer passenger seats, increasing at 3 dB per doubling of the number of passenger seats for airplanes having a seating configuration of three or more passenger seats. The noise limit for propeller-driven airplanes with three or more passenger seats can be calculated by the formula:
LAmax(G) = 74 + 10log(# PAX seats/2) dB for certifications obtained under 14 CFR part 36, Amendment 21 or earlier;
LAmax(G) = 77 + 10log(# PAX seats/2) dB for certifications obtained under 14 CFR part 36, Amendment 22 or later.

